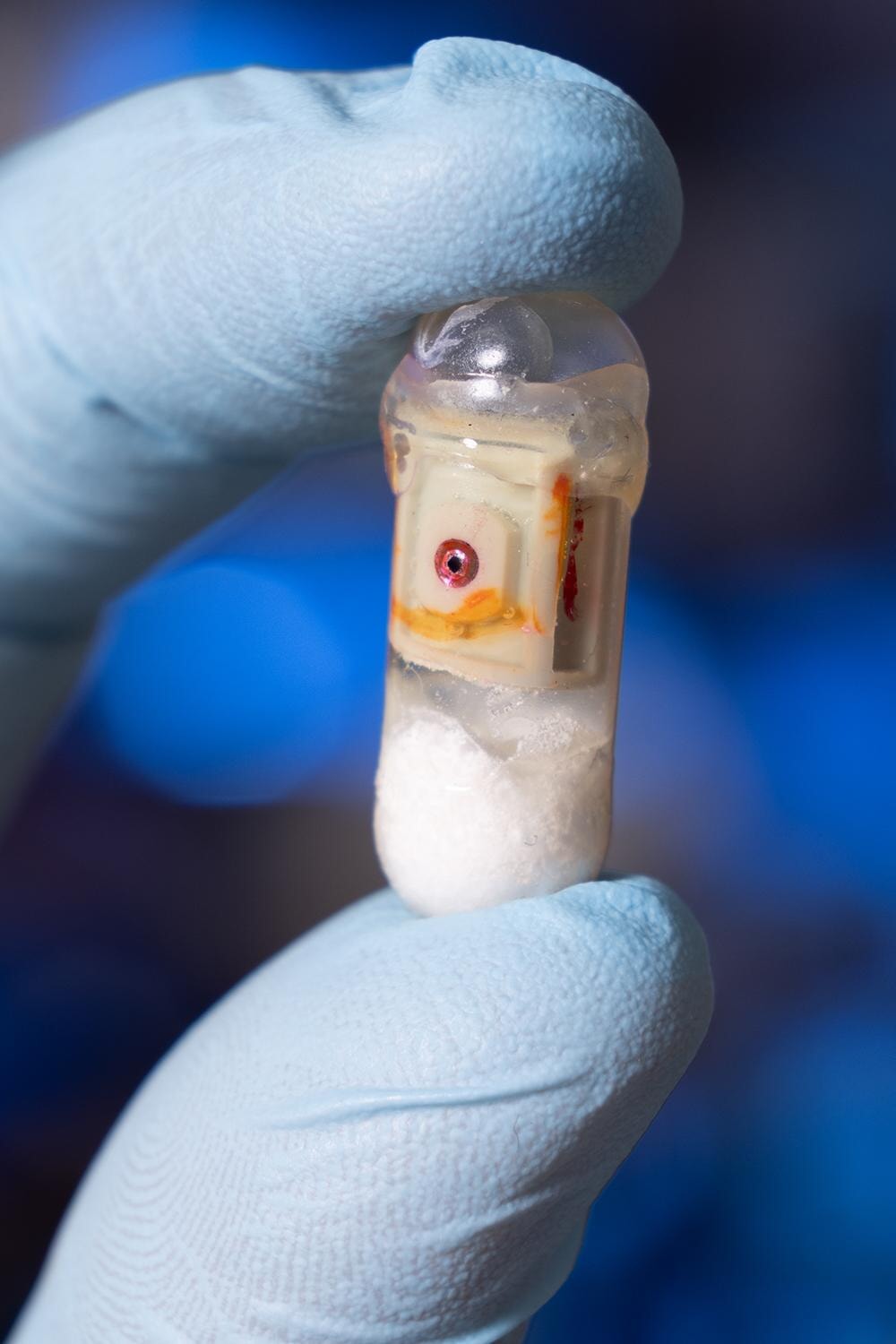
These Revolutionary 'Exploding Pills' Can Deliver Insulin Without a Needle
This is great news.
Published July 29, 2025
Advertisement
Advertisement
1. Needles, Fear, and a Better Way
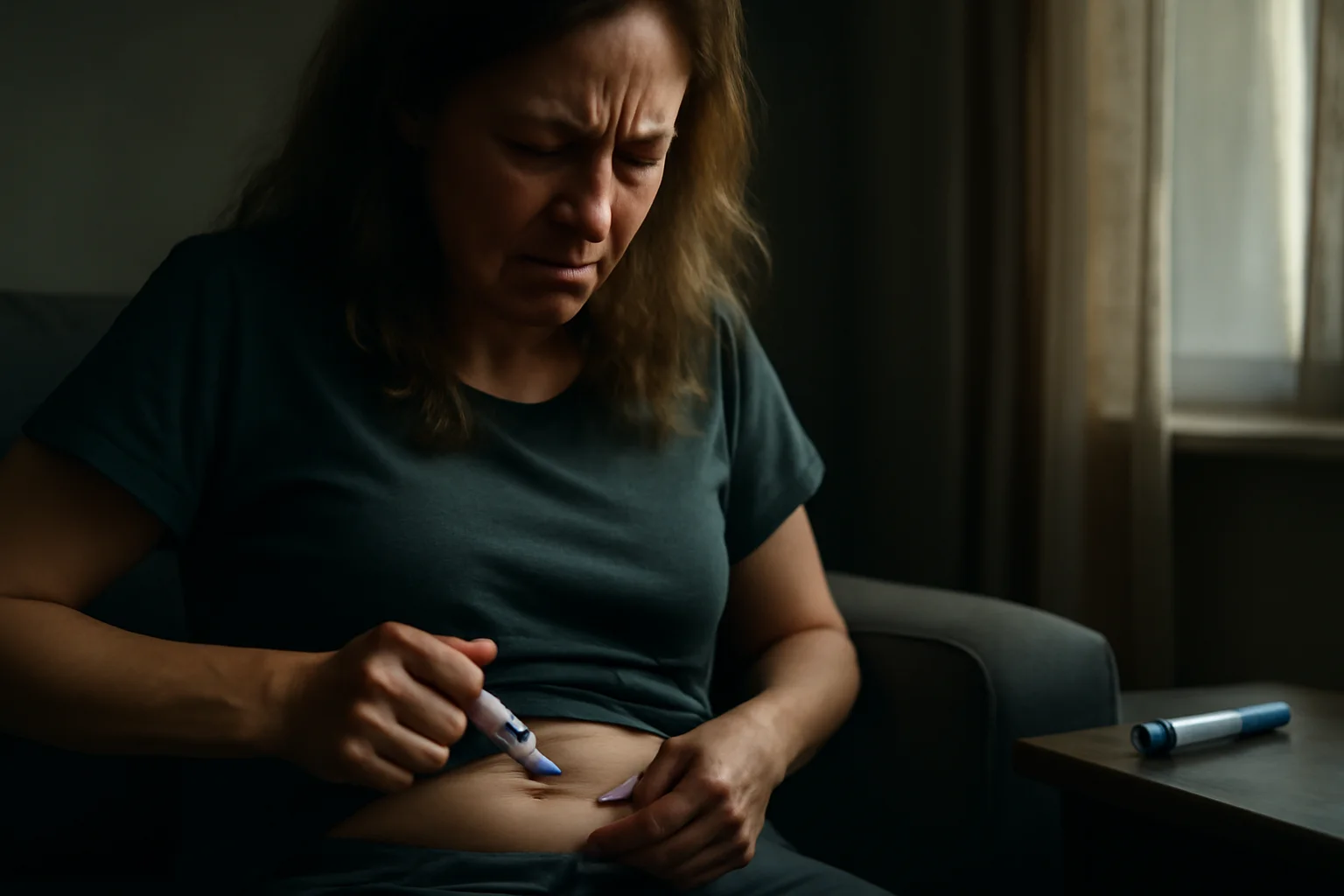

For millions living with chronic illnesses like diabetes, the daily or weekly ritual of injections is a burdensome constant—a prick that never fades, no matter how often endured.The routine of managing life-saving medications such as insulin, GLP-1 agonists like Ozempic and Wegovy, or even protein-based therapies for autoimmune conditions, is complicated not just by disease, but by the psychological and physical weight of the needle itself.Compliance falters, pain lingers, and the specter of infection or mishandling hovers over every injection, making it an ordeal rather than a solution.In the world of medicine, researchers have long recognized that injection-based treatments, while effective, create barriers for patients, discouraging consistent adherence and reducing the potential impact of powerful drugs.Many patients, young and old, avoid or delay their shots, and some simply give up—tired of the discomfort and the social stigma attached to visible syringes or injector pens.This unspoken struggle extends beyond diabetes, shadowing those with rheumatoid arthritis, growth hormone deficiencies, and myriad conditions requiring proteins or antibodies that the digestive system typically destroys.Scientists have dreamed for decades of an alternative—an easy, reliable pill that could replace injections without sacrificing effectiveness, safety, or affordability.Until recently, biology stood in the way: most of these molecules are fragile, easily broken down by stomach acid and digestive enzymes before they ever reach the bloodstream.The quest for a true oral alternative has generated countless ideas and prototypes, but few have survived the harsh gauntlet of the gastrointestinal tract.Still, necessity breeds innovation, and beneath the surface, a revolution in drug delivery has been gathering force.
Advertisement
2. Pills with a Punch
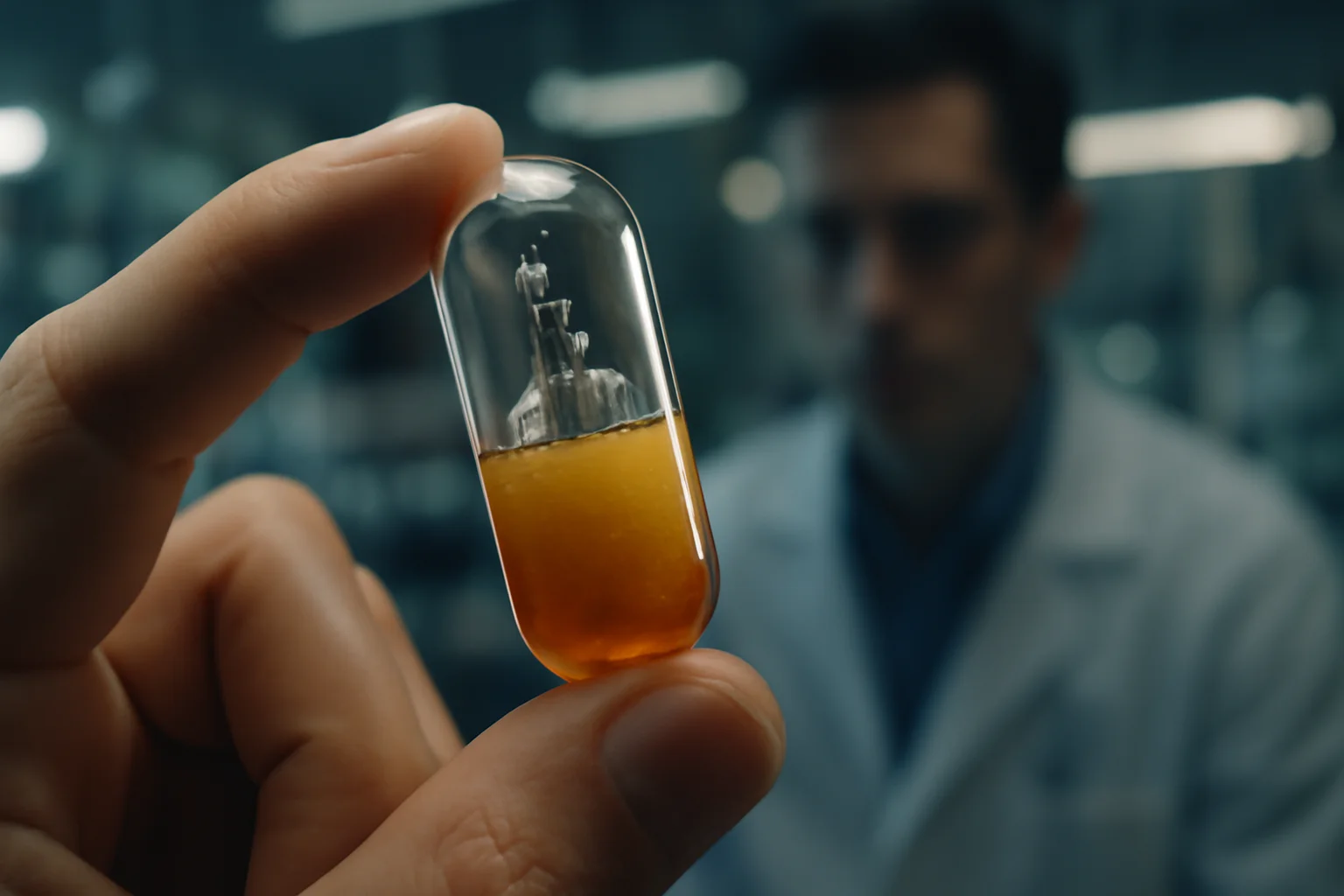

The dream of a needle-free future began to take tangible shape inside engineering labs at Georgia Tech and MIT, where two teams pursued bold new concepts for oral drug delivery.Both were united by a common goal: deliver delicate, injectable medications directly through the digestive wall, bypassing the destructive power of stomach acid and unlocking new possibilities for millions.At Georgia Tech, researchers harnessed simple chemistry—pairing sodium bicarbonate and citric acid inside a robust gelatin capsule—to create a “self-pressurizing” system.Once swallowed, the capsule waits until it reaches the small intestine, then triggers a controlled chemical reaction, building carbon dioxide pressure until a small membrane gives way.The result is a focused jet—a high-speed burst of medication fired directly into the tissue, crossing the mucus barrier and evading the enzymes eager to break it down.Meanwhile, at MIT, inspiration arrived from nature: cephalopods like squids and octopuses, whose jet-propelled escapes became the model for a microcapsule capable of pumping biologics into the walls of the GI tract.Whether powered by compressed gas or tightly wound springs, these tiny devices—about the size of a blueberry—release their medicine in a sharp, directed burst, creating a depot in the tissue for slow, steady absorption into the bloodstream.Both designs share an elegant simplicity: no batteries, no moving parts, just clever use of physical and chemical forces to overcome a seemingly intractable biological barrier.In animal studies, the results were dramatic—blood sugar dropped as effectively as with traditional injections, and no tissue damage was seen from the internal “explosions.”For the first time, scientists could imagine a pill not as a passive passenger, but as an active agent—capable of fighting its way past the gut’s defenses and into the body’s circulatory highway.
Advertisement
3. Lessons from Nature: Cephalopods and Tortoises
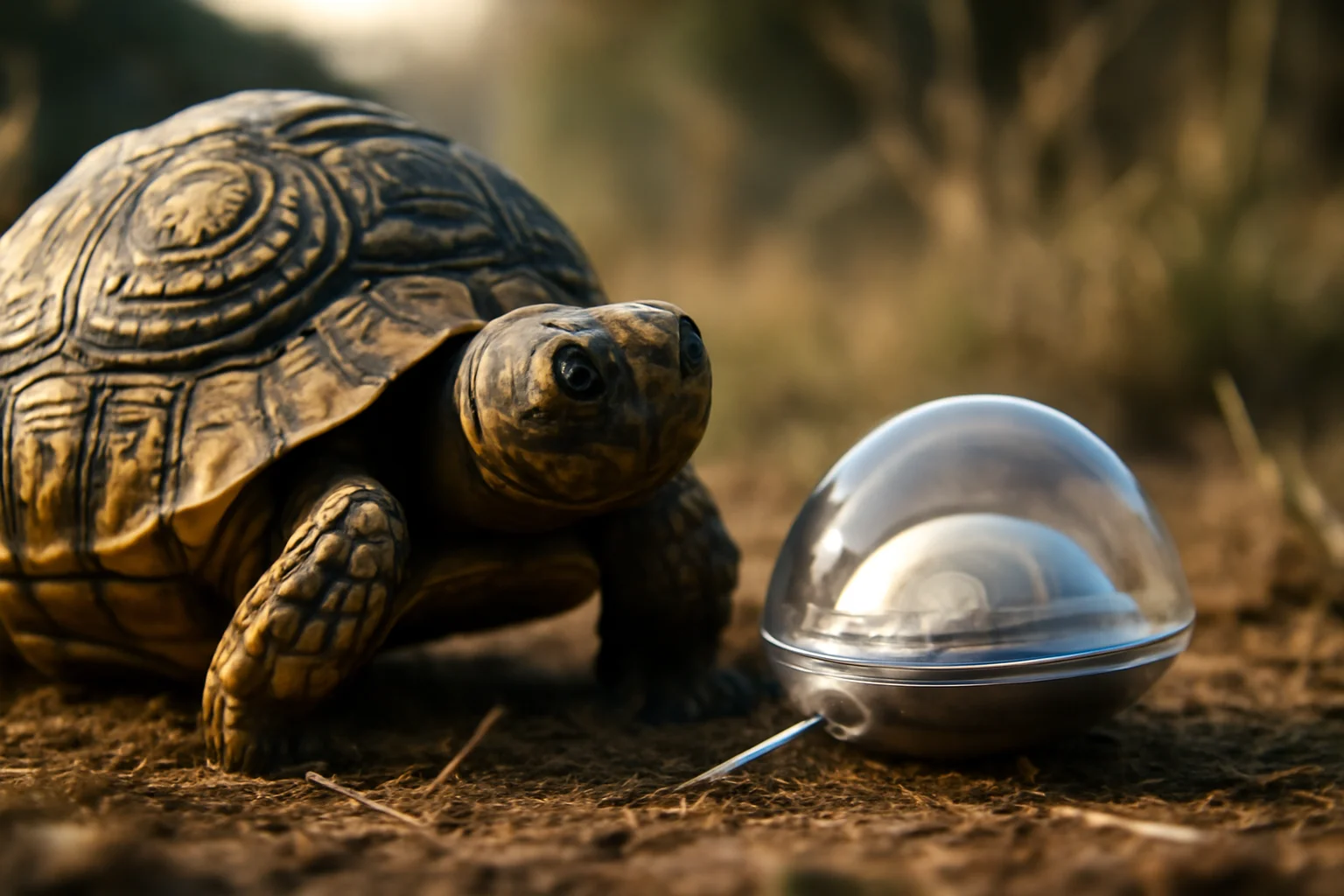

What does a leopard tortoise have in common with a diabetes pill? More than you might think, according to the MIT team responsible for a capsule that always lands needle-side down, ready to do its work.Inspired by the tortoise’s self-righting shell, researchers designed a dome-shaped device that can reorient itself no matter how it tumbles through the stomach.This innovation ensures that the delivery mechanism—whether a tiny jet or a dissolvable insulin needle—always faces the right way, ready to make contact with the tissue and inject its precious cargo.Elsewhere, cephalopod jet propulsion provided the blueprint for a needle-free system, propelling medication through a squirt of compressed gas, mimicking the precision and power of a squid escaping a predator.These bioinspired designs do more than make good stories; they solve real engineering challenges, providing robust, reliable orientation and targeted delivery in an unpredictable environment.For patients, these breakthroughs offer hope for a future where swallowing a pill could replace the ritual of lining up vials and syringes, no matter how complicated or sensitive the drug.The new capsules have been carefully constructed from biocompatible materials, with triggers that respond only to the right pH or humidity, ensuring that the burst happens exactly where it should—not in the mouth, not in the stomach, but in the small intestine.Each step of the way, researchers measured, modeled, and refined, seeking to balance power with safety, and targeting the right layer of tissue to create a lasting “depot” of medicine.Even the size and composition of the dose—down to the microgram—can be controlled, making these capsules adaptable to a range of biologics, from insulin to antibodies and beyond.It is a striking fusion of biology, physics, and patient-centered design.
Advertisement
4. Chemistry, Pressure, Precision
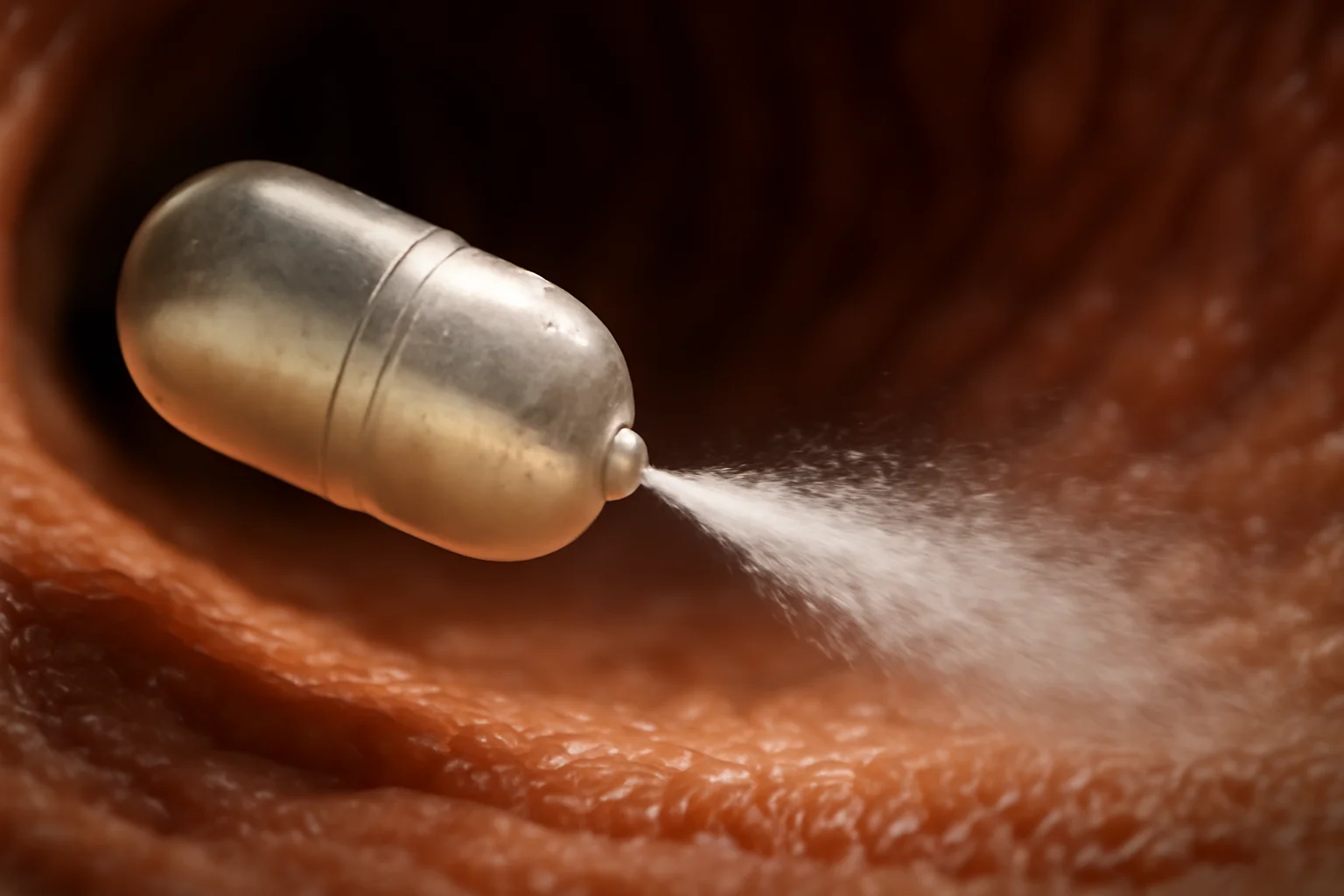

The basic challenge facing oral delivery of injectable drugs is not simply getting past the stomach, but outsmarting the complex series of defenses that have evolved to keep large molecules out.Proteins and RNA therapies are rapidly digested, their structures unraveled by acids and enzymes before they can ever reach the bloodstream.Traditional pills dissolve, releasing their contents into a hostile soup where nearly all is lost—just 1% of oral semaglutide, for example, ever makes it through intact.The new capsules, however, are built to resist this fate; their shells are strengthened, their mechanisms precisely tuned to rupture only at the target site, delivering a high-velocity jet that pushes the drug right up against the absorptive cells of the intestine.Because the medication moves so fast, it avoids the reach of protein-eating enzymes and is delivered right where it can slip into the bloodstream.The force is carefully calculated—enough to clear the protective mucus and deposit the drug, but not enough to damage the delicate lining.Animal studies have shown that these bursts do not cause irritation or injury, a crucial milestone in convincing regulators and physicians of their safety.This approach also makes the system robust to minor misalignments; unlike a needle, which needs to be in perfect contact, a jet can deliver most of its payload even if the capsule is slightly off-angle.Together, these advances mark a revolution not just in technology, but in our understanding of how to work with, rather than against, the body’s defenses.For millions awaiting a better option, the barriers may finally be coming down.
Advertisement
5. How Exploding Pills Change the Game
Only by the fifth act does the full mystery reveal itself: these “exploding” pills are not merely about convenience or novelty, but about transforming the very rules of drug delivery for chronic conditions.By blasting medication into the intestinal wall, these capsules bypass the obstacles that doomed previous oral biologics, achieving levels of absorption once thought impossible without a needle.The concept is deceptively simple—use pressure to inject, rather than dissolve and hope for the best.With this leap, medications once restricted to syringes—insulin, semaglutide, antibodies, growth hormone, even RNA-based therapies—could become candidates for easy, daily oral administration.No longer would patients need to schedule injections, refrigerate vials, or navigate the complexities of safe needle disposal.Clinical trials in animals have shown that glucose-lowering effects and blood concentrations of the drugs are comparable to traditional injections, without adverse tissue effects.By removing pain, hassle, and psychological barriers, adherence rises, outcomes improve, and treatment becomes part of daily routine instead of a weekly ordeal.The ripple effects are enormous: fewer skipped doses, fewer medical complications, less fear, and a dramatic reduction in medical waste.Suddenly, the quiet revolution happening inside the intestine is poised to reshape medicine on a global scale.
Advertisement
6. Pills for the Future
While diabetes and GLP-1 drugs are the first focus, the true potential of these capsules stretches far beyond a single disease.Protein drugs for arthritis, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, and countless other autoimmune or inflammatory conditions—many now delivered only by injection—could be reformulated for oral administration.MIT’s research demonstrated successful delivery of siRNA, a molecule used for gene silencing, which opens the door to treating rare genetic disorders in new ways.The modular design of the capsules allows for quick adaptation: needle or needle-free, vertical or lateral jets, large or small doses, single or combination therapies.There is even the possibility of endoscopic capsules, deployed directly to the target site by physicians, offering pinpoint precision for difficult-to-reach tumors or lesions.In the future, a medicine cabinet could hold not just tablets and liquids, but a new breed of “active” pills—engineered to cross boundaries, defeat barriers, and treat what was once untreatable.The environmental impact is significant too: no more sharps containers, no more syringes in landfills, no more risk of accidental sticks in clinics or homes.The implications for health systems are profound, from easier patient education to lower long-term costs.By reinventing the humble capsule, researchers have ignited a spark that could light the path for the next century of pharmaceuticals.
Advertisement
7. Animal Trials: First Proofs

Early animal studies have been the crucible in which these exploding pill concepts have been tested, refined, and validated.In both rats and pigs—chosen for their physiological similarities to humans—capsules consistently delivered effective doses of insulin and GLP-1 drugs, producing blood levels and glucose responses indistinguishable from subcutaneous injections.The new approach did not cause pain, thanks to the stomach wall’s lack of pain receptors, and did not trigger observable tissue irritation, inflammation, or bleeding.Safety was paramount, with each burst carefully monitored to avoid accidental damage, allergic reactions, or unwanted immune responses.Researchers tracked the capsules’ passage through the gut, confirming that all components were excreted naturally, leaving no harmful residue behind.They also demonstrated the ability to deliver multiple types of drugs from the same platform, highlighting the flexibility and adaptability of the technology.The feedback loop between laboratory, engineering, and clinical science has accelerated progress, moving the field rapidly toward the threshold of human trials.It is a testament to the collaborative spirit of academia, medicine, and industry, all racing to deliver a better answer for patients who have waited too long.As confidence grows and technical hurdles fall away, regulatory approval feels less like a distant dream and more like an imminent reality.
Advertisement
8. The Last Hurdle: Human Trials

The leap from animal success to human utility is never simple, and now the focus shifts to rigorous clinical testing.Regulators require not just efficacy and safety, but consistent manufacturing, predictable dosing, and long-term data on side effects or rare complications.Already, pharmaceutical giants like Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly are moving quickly, filing for FDA approval of oral formulations based on robust phase 3 trial data.For instance, oral Wegovy could soon become the first GLP-1 treatment in pill form for chronic weight management, while orforglipron—a daily pill for diabetes—has delivered impressive results in lowering A1C and promoting weight loss in large clinical trials.Each step toward approval brings the promise closer: soon, a visit to the pharmacy may include a prescription for a medication once thought possible only through injection.Still, questions remain about scale, cost, and how patients will embrace the idea of a pill that “explodes” inside their body—even if it does so quietly, safely, and invisibly.Education, transparency, and ongoing surveillance will be critical, as will the careful rollout to ensure every dose is as effective and gentle as the next.The race to the first oral biologics is on, and the world is watching.
Advertisement
9. Rethinking Medicine: Adherence, Environment, and Accessibility

Beyond the scientific fireworks, the true promise of exploding pills lies in their impact on patients’ lives and the broader healthcare landscape.Eliminating the needle barrier could transform medication adherence, especially for those who fear injections or struggle to maintain complex routines.A daily or weekly pill is easily integrated into morning rituals, fostering consistency and better long-term control of chronic conditions.The environmental advantages are compelling: fewer disposable syringes, no sharps waste, and less hazardous material for clinics and households to manage.There is also hope for lower manufacturing costs, since these capsules rely on inexpensive materials and established production lines, rather than high-tech injectors or bespoke packaging.For the developing world, where access to refrigeration and safe disposal is limited, oral biologics could unlock a new era of equitable care.If regulators, payers, and providers embrace the change, the ripple effects could be felt across continents and generations.Above all, the shift promises a gentler, more dignified experience for millions—restoring control, reducing stigma, and making medicine feel like care, not a chore.
Advertisement
10. A Pill That Breaks the Rules

The story of exploding pills is more than a technological marvel; it is a testament to human ingenuity, persistence, and the relentless pursuit of better answers.From the frustration of daily injections, to the inspiration found in cephalopods and tortoises, to the quiet triumphs of animal trials and the promise of human studies, each chapter marks a turning point in medicine.For the first time, the boundaries between what must be injected and what can be swallowed are dissolving, swept aside by pressure, precision, and creativity.Patients once limited by biology, fear, or circumstance stand on the threshold of a future where treatment is easier, safer, and more effective.Researchers are racing to broaden the scope, testing antibodies, growth hormones, and even RNA therapies—pushing the boundaries of what a simple capsule can do.As regulatory milestones approach and manufacturing scales up, the question for patients and providers is no longer “if” but “when.”Will you trust a pill to do the job of a needle? Would you welcome an “explosion” if it meant freedom from pain and hassle?For now, the revolution waits quietly inside medicine cabinets, but its impact is poised to echo through every corner of modern healthcare.This is how the future arrives—not with a bang you can hear, but with a burst of hope you can feel.
Advertisement
Advertisement
You May Also Like






