Nvidia and Foxconn Are in Talks to Bring Humanoid Robots to Their Factories
Are you ready?
Published June 30, 2025
Advertisement
Advertisement
1. The Birth of a New Manufacturing Era

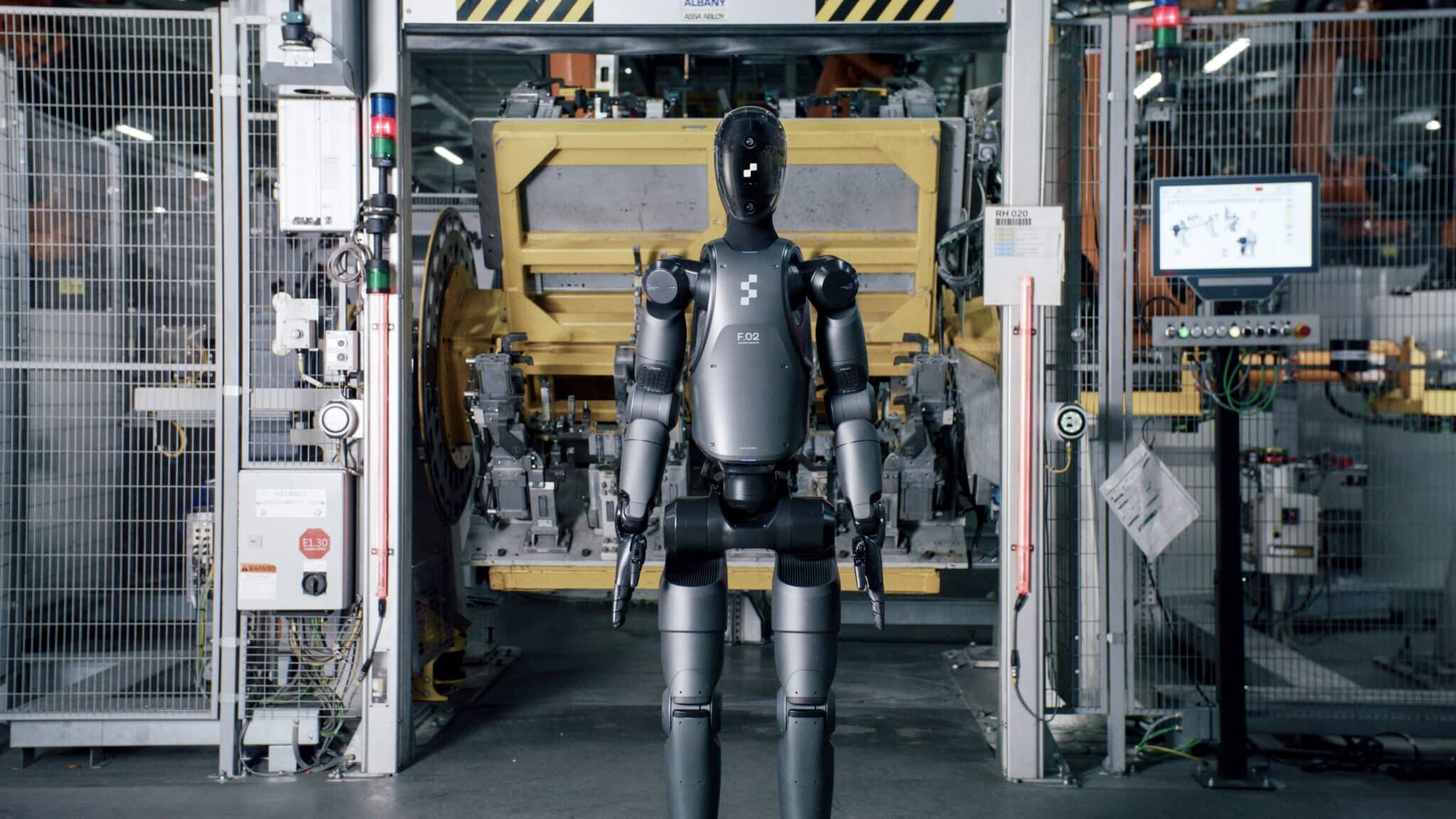
NVIDIA and Foxconn have embarked on a groundbreaking collaboration, aiming to introduce humanoid robots into Foxconn’s new factory in Houston, Texas, which will produce NVIDIA’s state-of-the-art AI servers.This partnership represents a historic first for both companies: NVIDIA products will be assembled with the assistance of humanoid robots, while Foxconn will debut this technology in its AI server production lines.The agreement, reportedly in advanced stages, is expected to be finalized within the next few months, with operations scheduled to commence as early as the first quarter of 2026.Industry sources emphasize the significance of this step, framing it as a milestone in both robotics and high-tech manufacturing.The Houston plant was chosen as the ideal launchpad, owing to its large, modern facilities, which provide ample space and resources for testing and deploying new robotics technologies.Foxconn and NVIDIA’s collaboration is not limited to this plant; the two have previously partnered on projects such as Taiwan’s first national AI supercomputing center.For NVIDIA, this move is both strategic and symbolic, strengthening its supply chain and supporting domestic manufacturing capabilities amid growing global competition for AI hardware.Foxconn, meanwhile, is actively developing its own humanoid robots in partnership with NVIDIA, while also evaluating models from other manufacturers like China’s UBTech.Though details about the exact models and their numbers remain under wraps, the robots are already being trained for assembly tasks such as picking and placing objects, inserting cables, and basic product construction.If successful, the project could radically alter the landscape of electronics manufacturing, setting a new benchmark for automation and efficiency in the AI era.NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang has repeatedly stated that widespread adoption of humanoid robots in manufacturing is less than five years away, underscoring the urgency and ambition behind this initiative.
Advertisement
2. Robotics on the Assembly Line
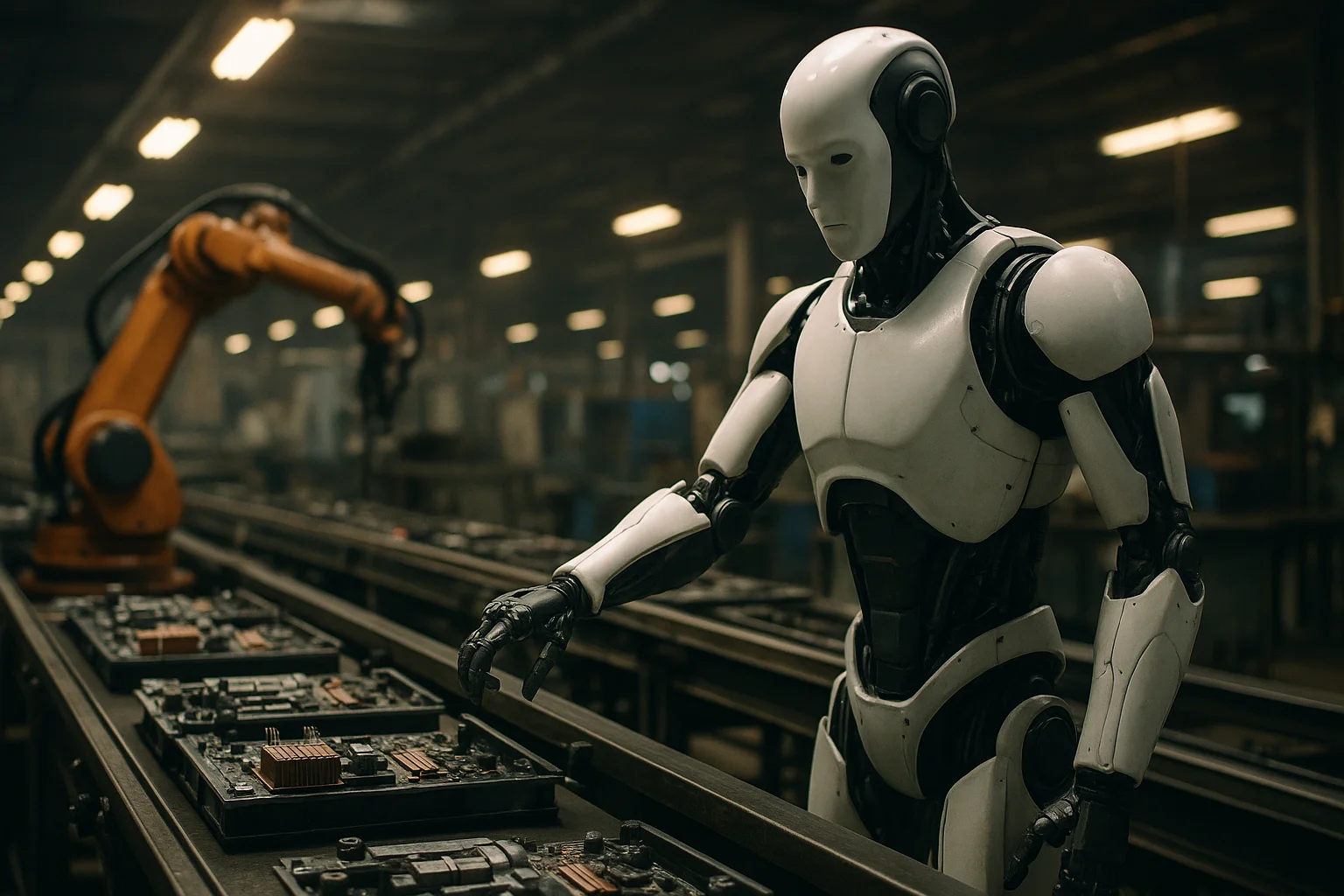

The concept of using robots in manufacturing is far from new, but the introduction of AI-driven humanoid robots marks a dramatic evolution in the automation of factory work.Foxconn has spent years perfecting its robotics technology, and is now poised to unveil two versions at a major technology event in November: one with a bipedal, legged frame, and another built on a wheeled autonomous mobile robot (AMR) base.While the legged version promises greater versatility and human-like movement, the wheeled model is expected to be more cost-effective for repetitive factory tasks.Both variants are being rigorously tested to ensure they can perform a range of assembly operations, from handling delicate components to moving heavy parts with precision.Foxconn’s presentation in May showcased early training programs, where robots practiced tasks central to server assembly, hinting at their imminent deployment in real production environments.The company’s experience with UBTech robots further expands its options, offering additional pathways for innovation and integration at the Houston facility.Despite the excitement, questions remain regarding how many robots will be deployed initially, what roles they will fulfill, and how seamlessly they will mesh with human workers and existing machinery.NVIDIA, for its part, already provides a robust robotics platform that manufacturers use to build humanoid robots, indicating that this factory project will also serve as a test bed for its technologies.Industry analysts suggest that humanoid robots could soon revolutionize not only manufacturing but also logistics, warehousing, and even customer service by leveraging their advanced mobility and dexterity.The ability of these robots to navigate cluttered environments and manipulate objects with human-like precision gives them an edge over traditional industrial automation.Ultimately, the Houston project could set a new global standard for the use of robotics in complex assembly lines, attracting attention from automakers and technology giants alike.
Advertisement
3. NVIDIA’s GB300 AI Servers and Next-Gen Hardware
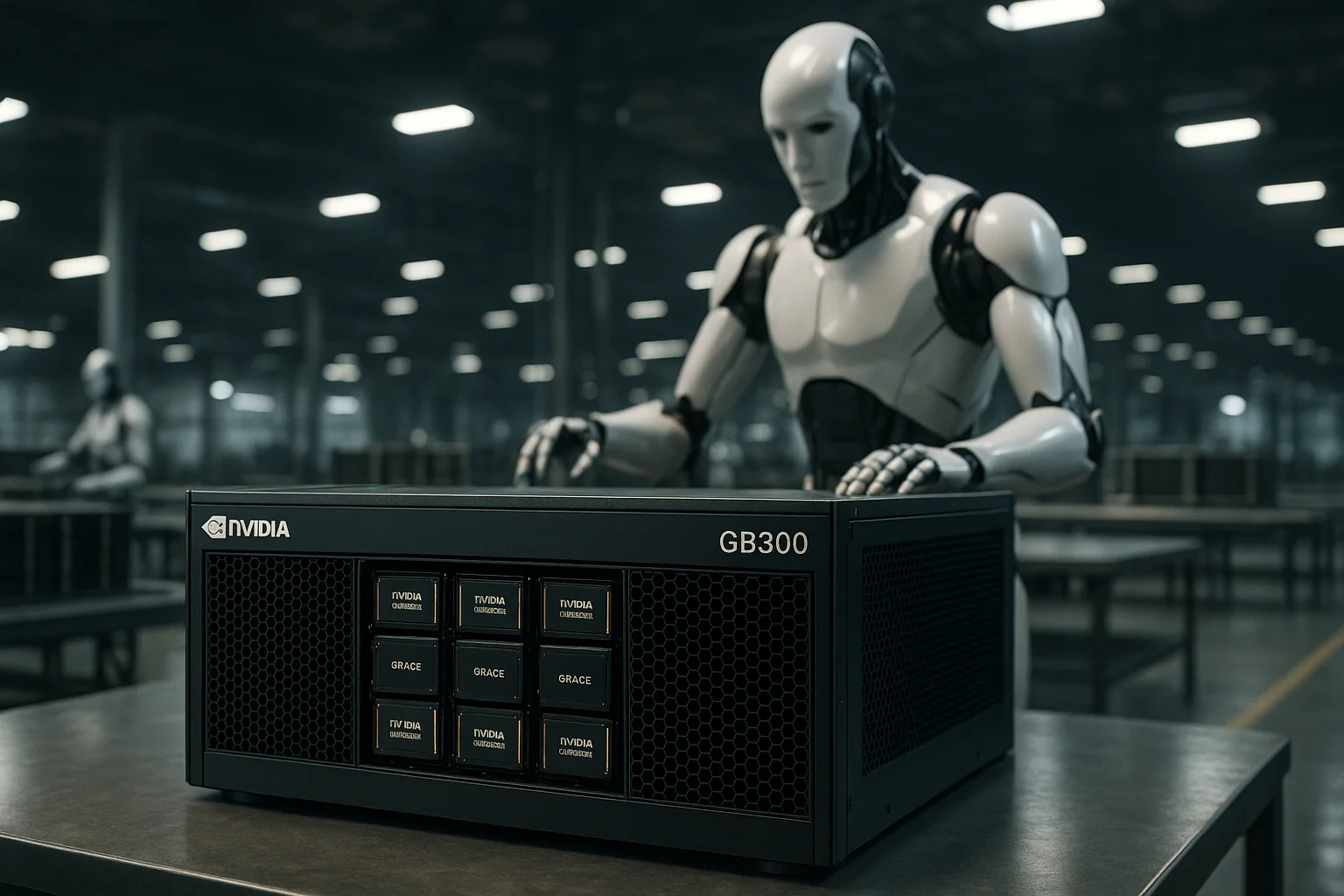

The primary product to be assembled by humanoid robots at the Houston plant is NVIDIA’s highly anticipated GB300 AI server.These servers represent the cutting edge of AI hardware, utilizing 72 NVIDIA Blackwell Ultra GPUs and 36 NVIDIA Grace CPUs to deliver unprecedented computational power.Designed for the most demanding AI models and workloads, the GB300 NVL72 excels not only in generative AI but also in agentic and physical AI applications, making it a cornerstone of future data centers.The integration of humanoid robots in the assembly process is expected to increase both speed and efficiency, driving down production costs while maintaining the highest standards of quality control.Foxconn’s Houston facility, with its advanced infrastructure and expansive floor space, offers an ideal environment for launching this new wave of automated manufacturing.The move to assemble these servers domestically marks a strategic shift for NVIDIA, allowing it to better meet surging demand while reducing its reliance on overseas production and supply chains.NVIDIA’s recent investments in U.S. manufacturing also reflect broader industry trends toward localization and resiliency in the wake of global disruptions and competitive pressures.By deploying humanoid robots, Foxconn and NVIDIA are betting that automation will not only accelerate output but also ensure greater consistency and fewer defects in their sophisticated products.Executives from both companies have highlighted the transformative potential of AI-powered robotics, viewing the GB300 production line as a proving ground for future expansions.The expected success of this initiative could trigger a wider robotics boom across the semiconductor industry, with ripple effects on how advanced computing hardware is produced worldwide.In this way, the Houston project is not just about one product, but about shaping the future of high-performance computing and automated assembly.
Advertisement
4. Training, Showcasing, and Scaling Robotics
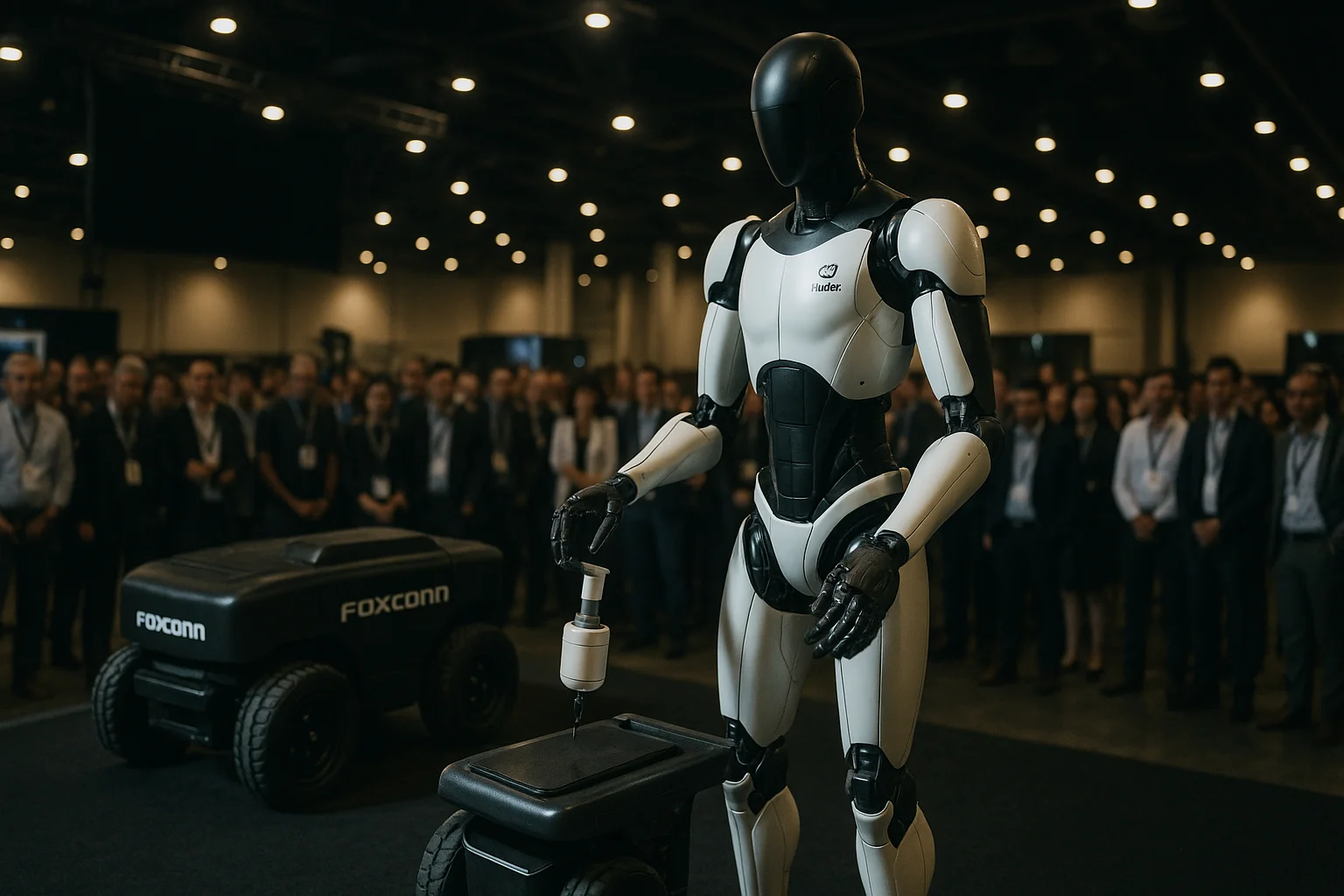

The deployment of humanoid robots in Houston is part of a broader strategy to train, evaluate, and showcase robotics technologies before scaling them globally.Foxconn has committed to presenting both its legged and wheeled robot prototypes at an annual technology event in November, providing industry observers with a first look at the future of factory automation.These demonstrations will be critical, as they offer tangible evidence of the robots’ capabilities and readiness for real-world deployment.Training programs have already begun, with robots learning essential manufacturing tasks such as object manipulation, cable insertion, and intricate assembly processes.By leveraging NVIDIA’s advanced robotics platform, Foxconn aims to accelerate the learning curve and maximize the operational value of its humanoid workforce.Foxconn’s collaboration with external partners like UBTech reflects a pragmatic approach, drawing from a global pool of expertise to optimize both hardware and software performance.The wheeled AMR base is viewed as an attractive option for high-throughput, repetitive tasks, while the legged model could be reserved for more complex, flexible operations that require human-like mobility.Industry analysts see these test runs as a vital step, providing data and feedback that will inform future iterations and wider rollouts of humanoid robots.If the Houston pilot succeeds, Foxconn may rapidly expand the use of humanoid robots to its other AI server plants and beyond, signaling a profound transformation in how electronics are built.In parallel, NVIDIA continues to advance its Isaac robotics research initiative, pushing the boundaries of what general-purpose, adaptable robots can achieve in data center environments.Together, these efforts are creating a roadmap for the scalable deployment of humanoid robots, from initial showcase to full production integration.
Advertisement
5. Pioneering the Isaac GR00T Platform

Central to NVIDIA’s robotics push is its Isaac GR00T platform, a fully customizable foundation model designed to bring generalized skills and reasoning to humanoid robots.GR00T N1 combines a fast-thinking “System 1” for reflexive actions and a deliberate “System 2” for complex, methodical planning—both inspired by human cognition.Developers and researchers can post-train GR00T N1 using real or synthetic data, enabling it to master specific tasks and adapt to varied factory environments.The platform’s vision language model allows robots to reason about their surroundings and instructions, planning actions dynamically rather than relying solely on preprogrammed routines.With these capabilities, GR00T N1 is well-suited for material handling, packaging, inspection, and multistep manufacturing tasks that require context-awareness and dexterity.Foxconn’s integration of the Isaac platform into its Houston facility serves as a real-world application and validation of NVIDIA’s technological ambitions.This approach opens new possibilities for customizing robots to perform highly specialized jobs, reducing the need for costly retooling and manual intervention on the assembly line.By facilitating both rapid reflexes and slow, strategic thinking, Isaac GR00T enables robots to handle everything from repetitive pick-and-place to complex, multistage processes.NVIDIA’s research into dual-system robotics is positioning the company as a leader not only in AI chips but also in the emerging field of physical AI.Foxconn’s collaboration with NVIDIA thus brings together hardware, software, and artificial intelligence to create a manufacturing environment that is both adaptive and scalable.If proven at scale, the Isaac GR00T framework could become the industry standard for deploying humanoid robots in production settings worldwide.
Advertisement
6. The Business Case and Global Context
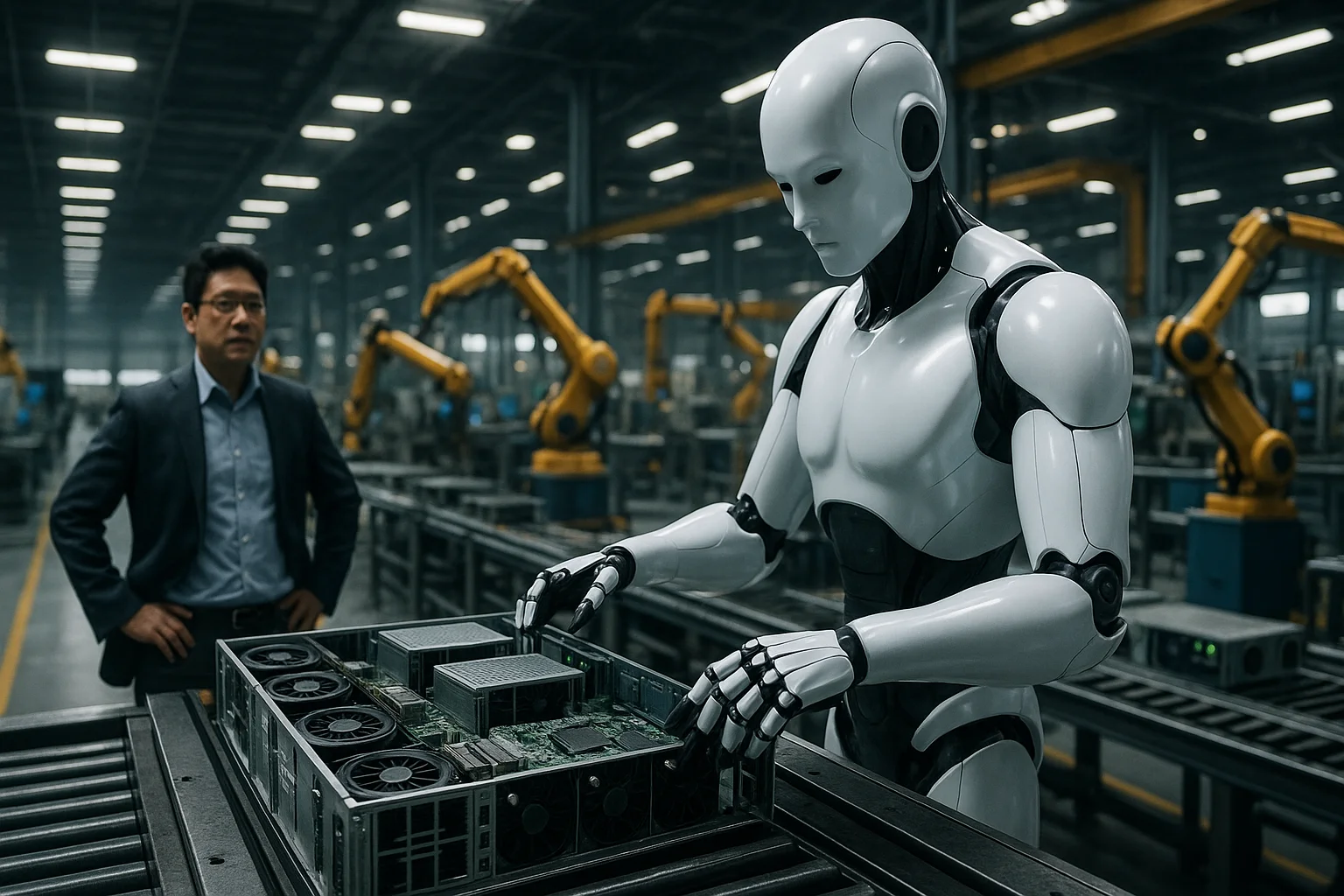

The Houston project emerges at a time of rapid change and fierce competition in the global AI hardware market.NVIDIA’s move to bring manufacturing to the United States is partly a response to supply chain disruptions, rising international tariffs, and the growing need for resilient domestic production.Foxconn’s strategy of investing in robotics aligns with trends among leading manufacturers, as automation becomes essential for meeting demand, reducing labor costs, and staying ahead of rivals.For NVIDIA, the domestic assembly of advanced AI servers provides a powerful marketing narrative, emphasizing reliability, security, and American innovation.The decision to incorporate humanoid robots into production also dovetails with efforts to address labor shortages and the increasing complexity of AI hardware assembly.Industry experts suggest that this approach could set a template for reshoring other forms of high-tech manufacturing to the U.S., supporting both economic growth and national competitiveness.Other major companies, such as Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Tesla, are also experimenting with humanoid robots on their production lines, indicating a broader shift toward intelligent automation.China’s heavy investment in humanoid robotics further underscores the global stakes, as companies and governments race to claim leadership in next-generation manufacturing.The Houston plant, by serving as a laboratory for innovation and a showcase for new technologies, positions both NVIDIA and Foxconn at the forefront of this international movement.If successful, the project could lead to a new wave of investment in robotics infrastructure and a reimagining of what it means to build the world’s most advanced electronics.As Jensen Huang and Foxconn executives frequently note, the next revolution in AI is not just digital, but physical, reshaping how ideas become reality in the modern factory.
Advertisement
7. Humanoid Robots: Promise and Challenges
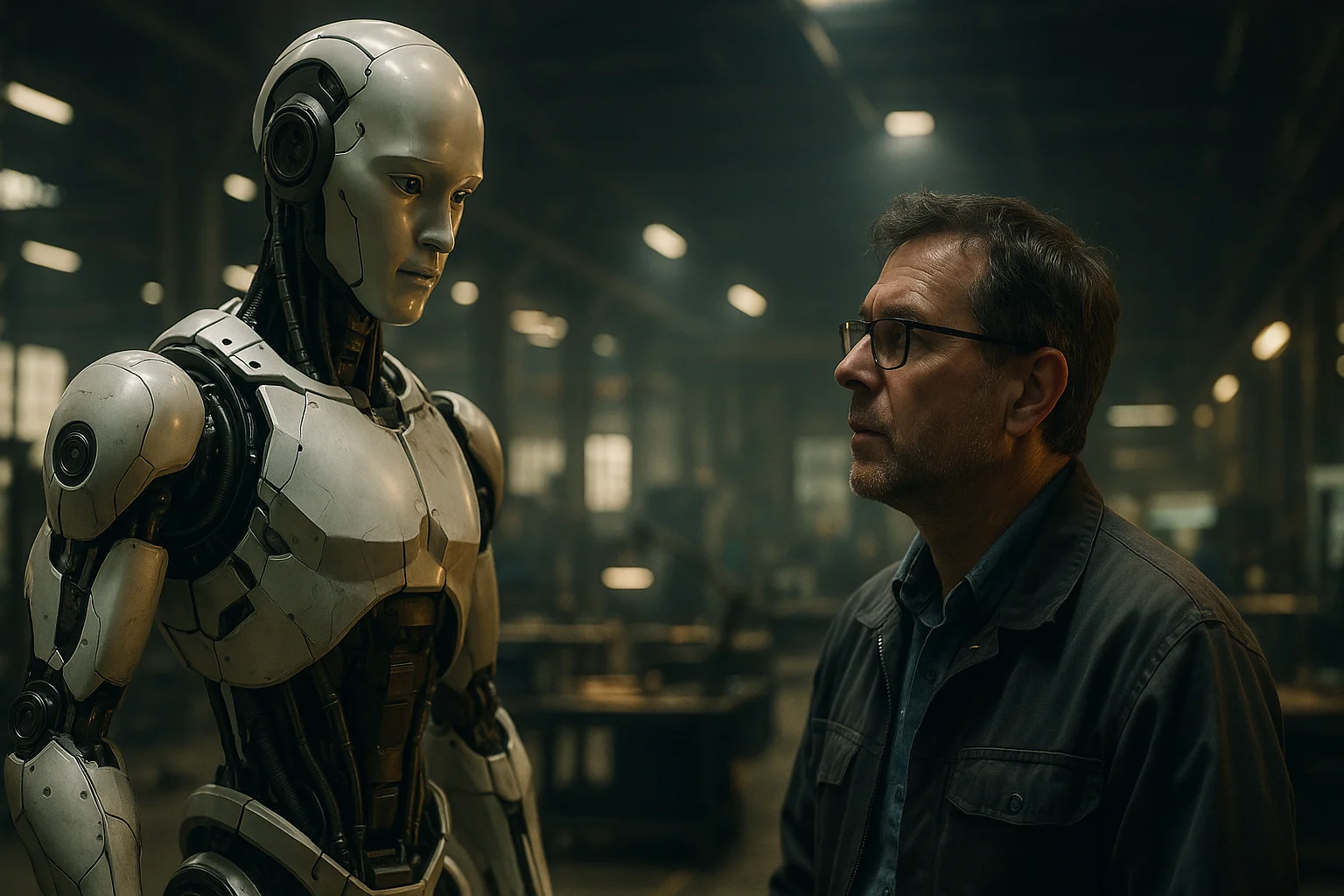

While the deployment of humanoid robots offers immense promise, it also brings a set of formidable challenges and open questions.Key uncertainties remain about the technical readiness of these robots, including their ability to integrate seamlessly with human teams and existing automated systems.Industry insiders note that while robots can handle repetitive tasks, adapting to unexpected changes or delicate assembly often still requires a human touch.The cost differential between legged and wheeled robots must also be weighed, as companies seek the right balance between versatility and affordability.Some skeptics in the automation community question whether humanoid forms are always necessary, suggesting that more specialized robotic arms or modular systems may suffice for certain tasks.Foxconn and NVIDIA must also address concerns about workforce displacement, ensuring that automation creates opportunities rather than simply replacing jobs.Training, maintenance, and cybersecurity for networked robots are additional hurdles that require careful planning and robust safeguards.Nevertheless, the rapid evolution of AI and robotics technologies means that many of today’s obstacles could be overcome with ongoing research, feedback from live deployments, and iterative improvements.Both companies are committed to transparent testing and continuous refinement, using the Houston facility as a real-world laboratory to tackle these issues head-on.Industry experts will be watching closely, as the success or failure of this pilot could shape investor sentiment and regulatory approaches to robotics in manufacturing.Despite the risks, the consensus is that the potential rewards—greater efficiency, higher quality, and a more resilient supply chain—make this experiment worth pursuing.
Advertisement
8. Industry Reactions and Broader Implications

News of the Foxconn-NVIDIA project has drawn significant attention from industry leaders, policymakers, and technology analysts.Many see the initiative as a bellwether for the future of manufacturing, where AI and robotics drive new levels of productivity and innovation.The move has been praised as a bold response to supply chain challenges and as a model for how companies can adapt to an era of global uncertainty.Others, however, urge caution, pointing to the high costs of automation, the technical challenges of deploying humanoid robots at scale, and the need for new regulatory frameworks.Automakers, semiconductor companies, and industrial giants are all closely monitoring the Houston project, seeing it as a potential template for their own automation strategies.Labor unions and workforce advocates are pressing for assurances that automation will be accompanied by upskilling, retraining, and investment in human capital.Government agencies in the U.S. and abroad are considering incentives and policies to support advanced manufacturing, recognizing its importance for economic resilience and national security.Academic researchers are eager to study the project’s outcomes, hoping to glean insights into the real-world performance of humanoid robots in high-stakes industrial environments.Startups and robotics firms view the initiative as a catalyst for new partnerships, pilot projects, and technological breakthroughs across the sector.For NVIDIA and Foxconn, the stakes are high: success could cement their leadership in both AI hardware and industrial automation, while failure could slow adoption and dampen investor enthusiasm.Regardless of the outcome, the Houston experiment will have far-reaching consequences for the future of work, technology, and global manufacturing.
Advertisement
9. The Path Ahead: Scaling and Replication
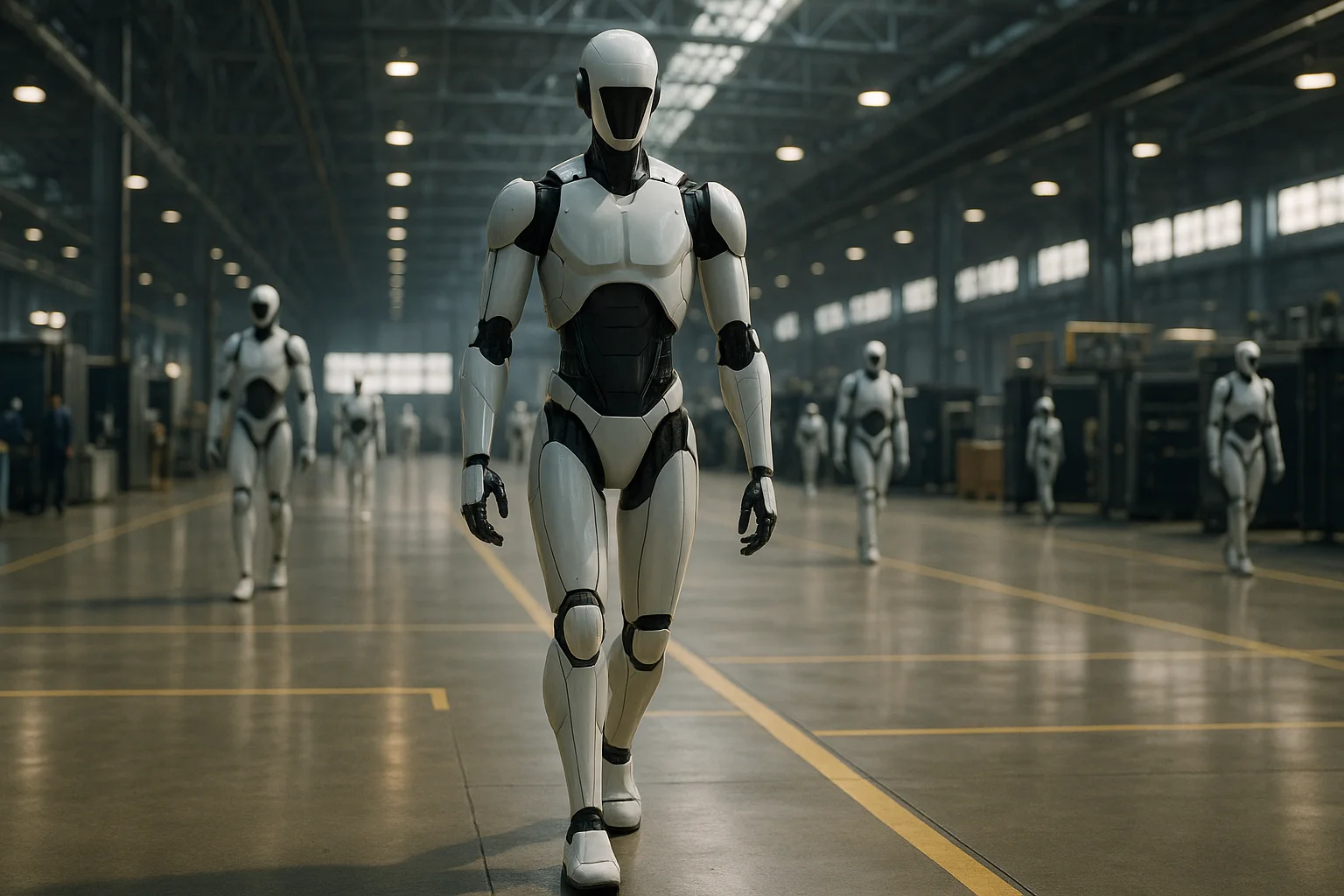

With the first wave of humanoid robots set to debut in Houston, both Foxconn and NVIDIA are already looking ahead to broader adoption and international scaling.Plans are in place to evaluate the performance of the robots through rigorous testing, collecting data on productivity, reliability, and integration with human workers.If results are positive, Foxconn is expected to expand humanoid robot deployment to additional AI server factories and possibly other product lines, both in the United States and globally.NVIDIA, meanwhile, aims to refine its Isaac GR00T platform, adapting it for diverse use cases and manufacturing environments based on lessons learned from Houston.Industry observers predict that successful scaling could trigger a domino effect, prompting rivals and partners alike to accelerate their own robotics initiatives.The ability to replicate and adapt this model across regions and industries could usher in a new era of distributed, automated manufacturing.Foxconn and NVIDIA’s willingness to share findings and best practices may also foster broader industry collaboration and accelerate standards-setting in robotics.Partnerships with universities, research labs, and government agencies could further amplify the impact, creating an ecosystem of innovation around intelligent automation.As the project matures, both companies will need to balance the pace of expansion with careful management of technical, logistical, and ethical considerations.The Houston plant thus represents both a proving ground and a springboard for a future in which humanoid robots are as common in factories as computers are in offices.
Advertisement
10. Transforming the Future of Manufacturing
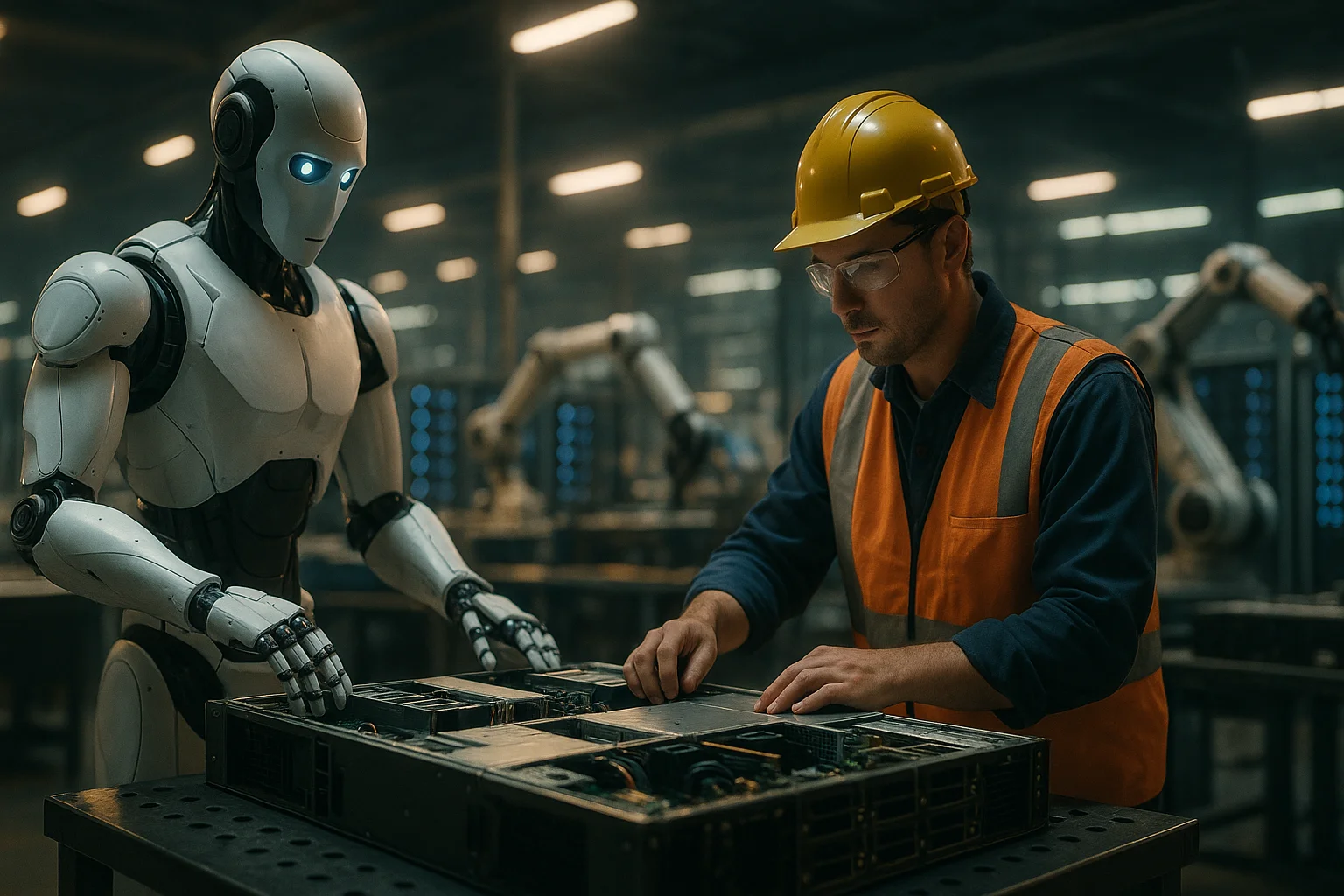

The collaboration between NVIDIA and Foxconn marks a turning point in the evolution of both robotics and advanced electronics manufacturing.By deploying humanoid robots in the assembly of cutting-edge AI servers, the two companies are laying the foundation for a new industrial paradigm defined by intelligent automation.This experiment is not just about building faster, cheaper, or more reliable products, but about reimagining the relationship between humans, machines, and the work of creation itself.The Houston project stands as a testament to the power of strategic partnerships, technological innovation, and a willingness to challenge conventional wisdom in pursuit of progress.It underscores the urgency of adapting to global shifts in labor, supply chains, and technology, while investing in the infrastructure needed to sustain future growth.The lessons learned in Houston will inform not only the next generation of factories, but also the broader digital transformation of the economy.Policymakers, business leaders, and workers alike will be watching closely, as the outcomes here could shape decisions about training, investment, and the very nature of work for decades to come.By integrating AI, robotics, and advanced manufacturing, NVIDIA and Foxconn are not just making servers—they are redefining what it means to build in the twenty-first century.As humanoid robots move from the realm of science fiction to the factory floor, their success in Houston could inspire a new wave of innovation across industries.Ultimately, this partnership is about harnessing technology to unlock human potential, creating factories of the future that are as intelligent, adaptable, and dynamic as the people and machines who bring them to life.
Advertisement
Advertisement
You May Also Like






